Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi
Kakushinteki Reikyaku Gijutsu; Mekanizumu Kara Soshi, Shisutemu Kaihatsu Made, p.179 - 183, 2024/01
The HTGR has excellent safety, and even in the event of an accident where the reactor coolant is lost, the decay heat and residual heat in the core can be dissipated from the outer surface of the RPV, so the fuel temperature never exceeds the limit value, and the core stabilizes. On the other hand, regarding the cooling system that transports the heat emitted from the RPV to the final heat sink, an active cooling system using forced circulation of water by a pump, etc., and a passive cooling system using natural circulation of the atmosphere have been proposed. However, there is a problem that the cooling performance is affected by the operation of dynamic equipment and weather conditions. This paper presents an overview of a new cooling system concept using radiative cooling, which has been proposed to solve the above problem, and introduces the results of analysis and experiments aimed at confirming the feasibility of this concept.
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/07
The stress intensity factor (SIF) for crack at nozzle corner is a key parameter in structural integrity assessment of nozzle in reactor pressure vessel (RPV). Although various SIF solutions for surface cracks at nozzle corners have been proposed, most of them are only focusing on the deepest point of the crack, and the information about geometric dimension of the nozzle corner is not clear. According to the previous fatigue test results regarding the surface crack at the nozzle corner, the amounts of crack growth at the surface points were larger than that at the deepest point of the crack. Such results imply that SIFs at the surface points may be higher than that at the deepest point. To increase the reliability of the structural integrity assessment, it is necessary to provide SIF solutions for both surface and deepest points. In this study, SIF solutions for two surface points and the deepest point of surface crack at nozzle corners are developed through finite element analyses and the solutions are provided corresponding to the geometric dimensions of nozzle corner and crack size.
Banno, Masaki*; Funatani, Shumpei*; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
A fundamental study on the safety of a passive cooling system for the RPV with radiative cooling is conducted. The object of this study is to demonstrate that passive RPV cooling system with radiative cooling is extremely safe and reliable even in the event of natural disasters. Therefore, an experimental apparatus, which is about 1/20 scale of the actual cooling system, was fabricated with several stainless steel containers. The surface of the heating element in the experimental apparatus simulates the surface of the RPV, and the heating element generates natural convection and radiation. A comparison of the Grashof number between the actual cooling system and the experimental apparatus confirmed that both were turbulent, and the experimental results as a scale model are valuable. Moreover, the experimental results confirmed that the heat generated from the surface of the RPV during the rated operation can be removed.
Yoshida, Kenta*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Shimodaira, Masaki
Materia, 62(3), p.154 - 158, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi*; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Li, Y.
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-006, 221 Pages, 2023/02
As a part of the structural integrity assessment research for aging light water reactor (LWR) components, a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR) has been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The PASCAL code can evaluate failure probabilities and failure frequencies of core region in reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transients by considering the uncertainties of influential parameters. The continuous development of the code aims to improve the reliability by introducing the analysis methodologies and functions base on the state-of-the-art knowledge in fracture mechanics and domestic data. In the first version of PASCAL, which was released in FY2000, the basic framework was developed for analyzing failure probabilities considering pressurized thermal shock events for RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs). In PASCAL Ver. 2 released in FY 2006, analysis functions including the evaluation methods for embedded cracks and crack detection probability models for inspection were introduced. In PASCAL Ver. 3 released in FY 2010, functions considering weld-overlay cladding on the inner surface of RPV were introduced. In PASCAL Ver. 4 released in FY 2017, we improved several functions such as the stress intensity factor solutions, probabilistic fracture toughness evaluation models, and confidence level evaluation function by considering epistemic and aleatory uncertainties related to influential parameters. In addition, the probabilistic calculation method was also improved to speed up the failure probability calculations. To strengthen the practical applications of PFM methodology in Japan, PASCAL code has been improved since FY 2018 to enable PFM analyses of RPVs subjected to a broad range of transients corresponding to both PWRs and boiling water reactors, including pressurized thermal shock, low-temperature over pressure, and normal operational transients. In particular, the stress intensi
Banno, Masaki*; Funatani, Shumpei*; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi
Yamanashi Koenkai 2022 Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2022/10
A fundamental study on the safety of a passive cooling system for the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) with radiative cooling is conducted. The object of this study is to demonstrate that passive RPV cooling system with radiative cooling is extremely safe and reliable even in the event of natural disasters. Therefore, an experimental apparatus, which is about 1/20 scale of the actual cooling system, was fabricated with several stainless steel containers. The surface of the heating element in the experimental apparatus simulates the surface of the RPV, and the heating element generates natural convection and radiation. As a result of the experiments, we succeeded in visualizing the natural convection in the experimental apparatus in detail.
Zarazovski, M.*; Pistra, V.*; Lauerova, D.*; Obermeier, F.*; Mora, D.*; Dubyk, Y.*; Bolinder, T.*; Cueto-Felgueroso, C.*; Szavai, S.*; Dudra, J.*; et al.
Proceedings of ASME 2022 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2022) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/07
Madokoro, Hiroshi; Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Gaus-Liu, X.*; Cron, T.*; Fluhrer, B.*; St ngle, R.*; Wenz, T.*; Vervoortz, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya
ngle, R.*; Wenz, T.*; Vervoortz, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 16 Pages, 2022/03
Shimodaira, Masaki; Tobita, Toru; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Hanawa, Satoshi
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011304_1 - 011304_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Mechanical)In the structural integrity assessment of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV), the fracture toughness (K ) should be higher than the stress intensity factor at the crack tip of an under-clad crack (UCC), which is prescribed in JEAC4206-2016. However, differences in crack depth and existence of cladding between the postulated crack and fracture toughness test specimens would be affected to the plastic constraint state and K
) should be higher than the stress intensity factor at the crack tip of an under-clad crack (UCC), which is prescribed in JEAC4206-2016. However, differences in crack depth and existence of cladding between the postulated crack and fracture toughness test specimens would be affected to the plastic constraint state and K evaluation. In this study, we performed fracture toughness tests and finite element analyses (FEAs) to investigate the effect of cladding on K
evaluation. In this study, we performed fracture toughness tests and finite element analyses (FEAs) to investigate the effect of cladding on K evaluation. FEA showed that the cladding decreased the plastic constraint in the UCC rather than the surface crack. Moreover, it was also found that the apparent K
evaluation. FEA showed that the cladding decreased the plastic constraint in the UCC rather than the surface crack. Moreover, it was also found that the apparent K for the UCC was higher than that for the surface crack from tests and the local approach.
for the UCC was higher than that for the surface crack from tests and the local approach.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hata, Kuniki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153203_1 - 153203_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Solute clusters (SCs) formed in pressurized water reactor surveillance test specimens neutron-irradiated to a fluence of 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius (
were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius ( ) and number density (
) and number density (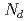 ) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition (
) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition ( RT
RT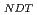 ) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (
) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (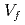 ) multiplied by r (
) multiplied by r (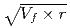 ). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and
). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and  RT
RT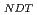 indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(5), p.051502_1 - 051502_8, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.36(Engineering, Mechanical)no abstracts in English
Shimodaira, Masaki; Tobita, Toru; Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/07
In the structural integrity assessment of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV), the fracture toughness (K ) should be higher than the stress intensity factor at the crack tip of a semi-elliptical shaped under-clad crack (UCC), which is prescribed in JEAC4206-2016. However, differences in crack depth and existence of cladding between the postulated crack and fracture toughness test specimens would be affected to the plastic constraint state and K
) should be higher than the stress intensity factor at the crack tip of a semi-elliptical shaped under-clad crack (UCC), which is prescribed in JEAC4206-2016. However, differences in crack depth and existence of cladding between the postulated crack and fracture toughness test specimens would be affected to the plastic constraint state and K evaluation. In this study, we performed fracture toughness tests and finite element analyses to investigate the effect of plastic constraint and cladding on the semi-elliptical shaped crack in K
evaluation. In this study, we performed fracture toughness tests and finite element analyses to investigate the effect of plastic constraint and cladding on the semi-elliptical shaped crack in K evaluation. The apparent K
evaluation. The apparent K value evaluated at the deepest point of the crack exceeded 5% fracture probability based on the Master Curve method estimated from C(T) specimens, and the conservativeness of the current integrity assessment method was confirmed. Few initiation sites were observed along the tip of semi-elliptical shaped crack other than the deepest point. The plastic constraint state was also analyzed along the crack tip, and it was found that the plastic constraint at the crack tip near the surface was lower than that for the deepest point. Moreover, it was quantitatively showed that the UCC decreased the plastic constraint. The local approach suggested higher K
value evaluated at the deepest point of the crack exceeded 5% fracture probability based on the Master Curve method estimated from C(T) specimens, and the conservativeness of the current integrity assessment method was confirmed. Few initiation sites were observed along the tip of semi-elliptical shaped crack other than the deepest point. The plastic constraint state was also analyzed along the crack tip, and it was found that the plastic constraint at the crack tip near the surface was lower than that for the deepest point. Moreover, it was quantitatively showed that the UCC decreased the plastic constraint. The local approach suggested higher K value for the UCC than that for the surface crack, reflecting the low constraint effect for the UCC.
value for the UCC than that for the surface crack, reflecting the low constraint effect for the UCC.
Li, Y.; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Itabashi, Yu*; Yamamoto, Masato*; Kanto, Yasuhiro*; Suzuki, Masahide*; Miyamoto, Yuhei*
JAEA-Review 2020-011, 130 Pages, 2020/09
For the improvement of the structural integrity assessment methodology on reactor pressure vessels (RPVs), the probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed and improved in Japan Atomic Energy Agency based on the latest knowledge. The PASCAL code evaluates the failure probabilities and frequencies of Japanese RPVs under transient events such as pressure thermal shock considering neutron irradiation embrittlement. In order to confirm the reliability of the PASCAL as a domestic standard code and to promote the application of PFM on the domestic structural integrity assessments of RPVs, it is important to perform verification activities, and summarize the verification processes and results as a document. On the basis of these backgrounds, we established a working group, composed of experts on this field besides the developers, on the verification of the PASCAL module and the source program of PASCAL was released to the members of working group. This report summarizes the activities of the working group on the verification of PASCAL in FY2016 and FY2017.
 WB-STEM observation of dislocation loop behavior in reactor pressure vessel steel during post-irradiation annealing
WB-STEM observation of dislocation loop behavior in reactor pressure vessel steel during post-irradiation annealingDu, Y.*; Yoshida, Kenta*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Milan, K. J.*; Gerard, R.*; Onuki, Somei*; et al.
Materialia, 12, p.100778_1 - 100778_10, 2020/08
In order to ensure the integrity of the reactor pressure vessel in the long term, it is necessary to understand the effects of irradiation on the materials. In this study, irradiation-induced dislocation loops were observed in neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel specimens during annealing using our newly developed WB-STEM. It was confirmed that the proportion of 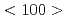 loops increased with increasing annealing temperature. We also succeeded in observing the phenomenon that two
loops increased with increasing annealing temperature. We also succeeded in observing the phenomenon that two 
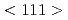 loops collide into a
loops collide into a 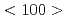 loop. Moreover, a phenomenon in which dislocation loops decorate dislocations was also observed, and the mechanism was successfully explained by molecular dynamics simulation.
loop. Moreover, a phenomenon in which dislocation loops decorate dislocations was also observed, and the mechanism was successfully explained by molecular dynamics simulation.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Lu, K.; Mano, Akihiro; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2020/08
We have developed a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL4 for evaluating failure frequency of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). It is known that flaw distributions have an important role in failure frequency calculation in PFM analysis. Previously, we proposed likelihood function to obtain more realistic flaw distributions applicable for both case when flaws are detected and when there is no flaw indication as the inspection results based on Bayesian update methodology. Here, it can be applied to independently obtain posterior distributions of flaw depth and density. In this study, we improve the likelihood function to enable them to update flaw depth and density simultaneously. Based on the improved likelihood function, an example is presented in which flaw distributions are estimated by reflecting NDI results through Bayesian update and PFM analysis. The results indicate that the improved likelihood functions are useful for estimating flaw distributions.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Hirano, Takashi*
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Ha, Yoosung; Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2019 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/07
no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Jinya; Uno, Shumpei*; Watanabe, Tadashi*; Li, Y.
Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 13(4), p.563 - 570, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.21(Engineering, Mechanical)For the structural integrity assessments on reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) under pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events, thermal hydraulic (TH) behavior of coolant water is one of the most important influence factors. Configuration of plant equipment and their dimensions, and operator action have large influences on TH behavior. In this study, to investigate the influence of operator action on TH behavior during a PTS event, we developed an analysis model for a typical Japanese plant, and performed TH and structural analyses. Two different operator action times were assumed based on the Japanese and US' rules. From the analysis results, it was clarified that differences in operator action times have a significant effect on TH behavior and loading conditions, that is, following the Japanese rule may lead to lower stresses compared to that when following the US rule because earlier operator action caused lower pressure in the RPV.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Li, Y.
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-015, 229 Pages, 2018/03
As a part of the structural integrity research for aging light water reactor components, a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed in JAEA. The PASCAL code can evaluate the conditional failure probabilities and failure frequencies for core region in reactor pressure vessels under the pressurized thermal shock events. In this study, we improved many functions such as the stress intensity factor solutions, the fracture toughness models, or confidence level evaluation function by considering epistemic and aleatory uncertainties related to influence parameters in the structural integrity assessment. We also developed the analysis module PASCAL-Manager which calculates the failure frequency for the entire core region taking into consideration the failure probabilities obtained from PACAL-RV. Based on these improvements, the new analysis code is upgraded to PASCAL Ver.4. This report provides the user's manual and theoretical background of PASCAL Ver.4.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2016-022, 40 Pages, 2017/02
For reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in the light water reactors, the fracture toughness decreases due to the neutron irradiation embrittlement with operating years. In Japan, to prevent RPVs from a nil-ductile fracture, deterministic fracture mechanics methods in accordance with the codes provided by the Japan Electric Association are performed for assessing the structural integrity of RPVs under the pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events by taking the neutron irradiation embrittlement into account. On the other hand, in recent years, probabilistic methodologies for PTS evaluation are introduced into regulations in Europe and the United States. For example, in the United States, a PTS screening criterion related to the reference temperature derived by the probabilistic method is stipulated. If the screening criterion is not satisfied, it is approved to perform the evaluation based on the probabilistic method by calculating numerical index such as through-wall crack frequency (TWCF). To reach the objectives that persons who have knowledge on the fracture mechanics can carry out the PFM analyses and obtain TWCF for a domestic RPVs by referring to this report, we develop the guideline on a structural integrity assessment method based on PFM by reflecting the latest knowledge and expertise.